A* Algorithm(길찾기 알고리즘) Unity3D로 구현하기
이론
A* 알고리즘 (AStar Algorithm, 에이 스타 알고리즘)은 주어진 출발지에서, 목적지까지 가는 최단 경로를 찾아내기 위해 고안된 그래프 탐색 알조리즘 중 하나이다.
이는 최단의 경로를 탐색하기 위하여 휴리스틱 추정값($h(n)$)을 매기는 방법을 사용한다.
$ f(n) = g(n) + h(n) $
- $g(n)$ : 출발지점으로부터 \(n\)까지의 경로값
- $h(n)$ : $n$부터 목적지점까지의 경로값
방식
OPEN // 값을 정하기 전의 노드의 집합
CLOSED // 값이 정해진 노드의 집합
add start node to OPEN
loop
current = OPEN 포함 된 노드중 fCost가 가장 작은 노드
remove current from OPEN
add current to CLOSED
if current == target node
return
foreach neighbour of the current node
if neighbour node이 통과 불가능하거나, CLOSED에 포함되어 있을 시
continue
set fCost of neighbour
set parent of neighbour to current
if neighbour is not in OPEN
add neighbour to OPEN
- 노드(node) : 데이터를 가지고 있는 가장 기초적인 단위를 뜻한다. A* 알고리즘 에서는 fCost, 이동가능여부 등의 정보를 가지고 있다.
길찾기 알고리즘을 구현할 때는 그리드(grid)형식을 사용하여 노드간의 거리가 일정한 방식을 사용한다.
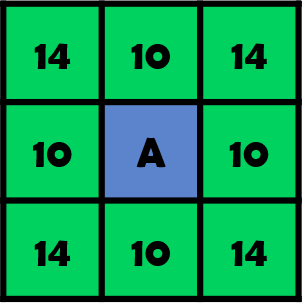
A가 현재의 노드일 때, 주변 8칸의 이웃(neighbour)하는 노드가 존재 합니다. 상하좌우의 크기를 10이면, 대각선은 피타고라스 정리에 의해서 14의 근사값을 가지게 됩니다.
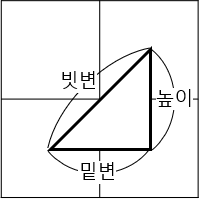 $$\sqrt{밑변^2+높이^2} = 빗변 => \sqrt{10^2 + 10^2} = \sqrt{200} = 14.142135...$$
$$\sqrt{밑변^2+높이^2} = 빗변 => \sqrt{10^2 + 10^2} = \sqrt{200} = 14.142135...$$그림설명 접기/펼치기
A에서 B로 이동하기 위한 상황. 검은색 노드는 장애물을 의미한다.
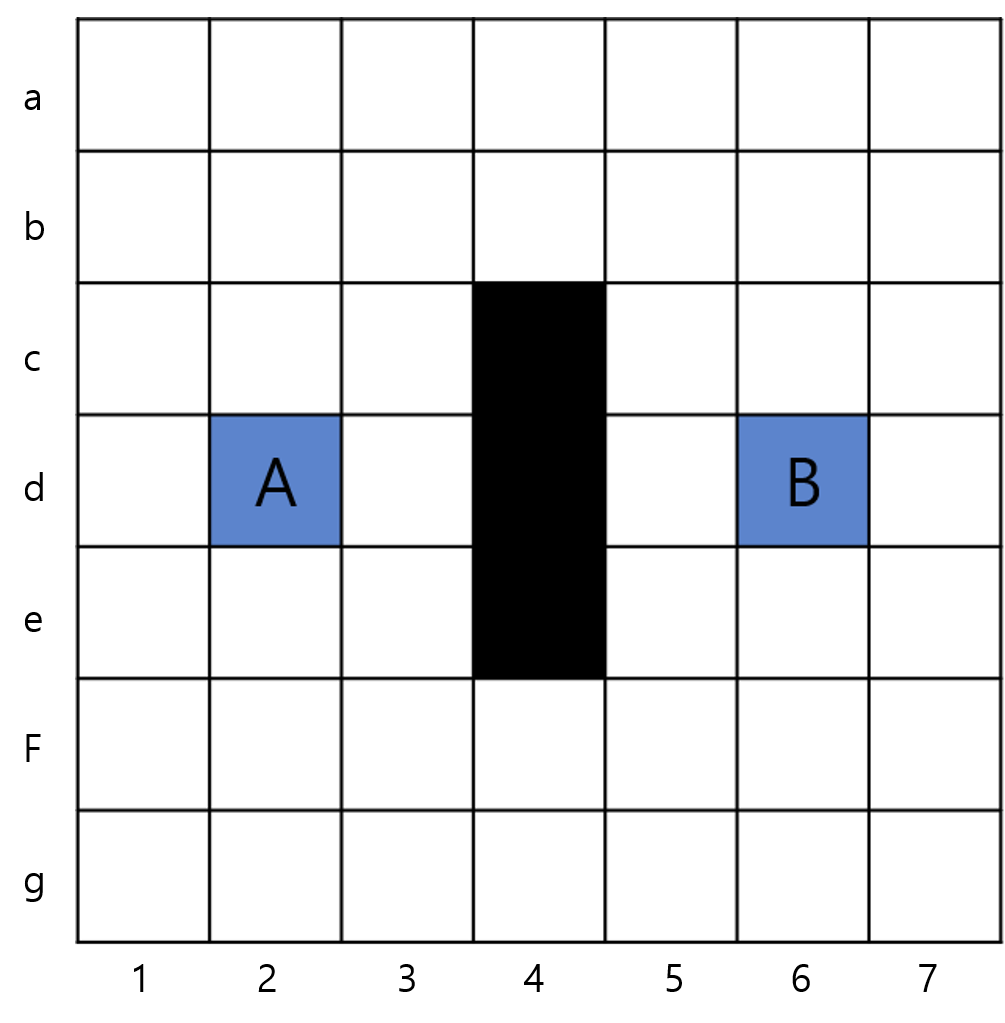
- OPEN = (+d2)
- CLOSE =

- A의 주변 노드들의 fCost를 구한다. (11시 gCost, 1시 hCost, 6시 fCost)
- neighbour = {c1, c2, c3, d1, d3, e1, e2, e3}, 8개의 노드는 d2의 부모를 가진다.
- OPEN = (-d2), (+c1, c2, c3, d1, d3, e1, e2, e3)
- CLOSE = (+d2)
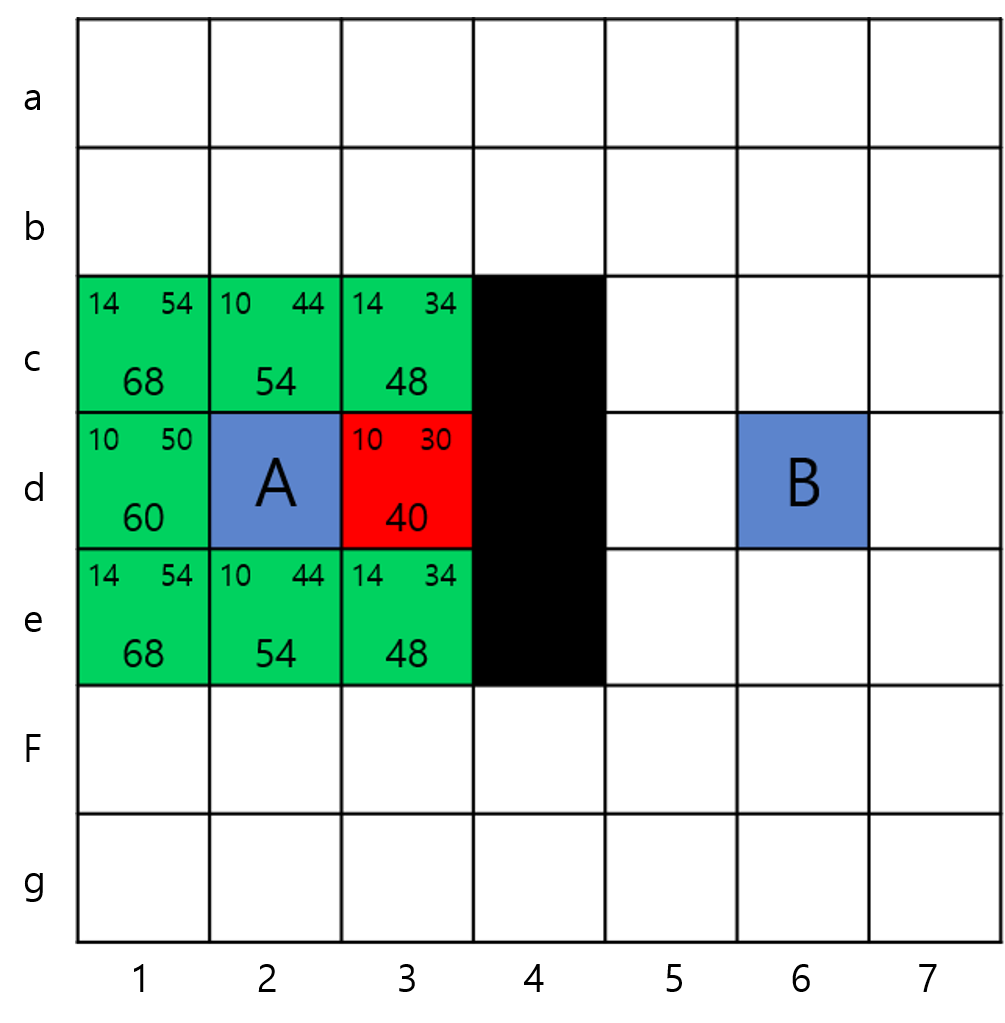
- OPEN 에 포함된 노드중 가장 작은 fCost를 가진 노드인 d3를 기준으로 계산한다.
- d3의 경우 주변 8개의 노드가 ‘OPEN(c2, c3, e2, e3), CLOSE(d2), 이동불가노드(c4, d4, e4)’에 포함되어있어 변화가 없다.
- OPEN = c1, c2, c3, d1, e1, e2, e3, (-d3)
- CLOSE = d2, (+d3)
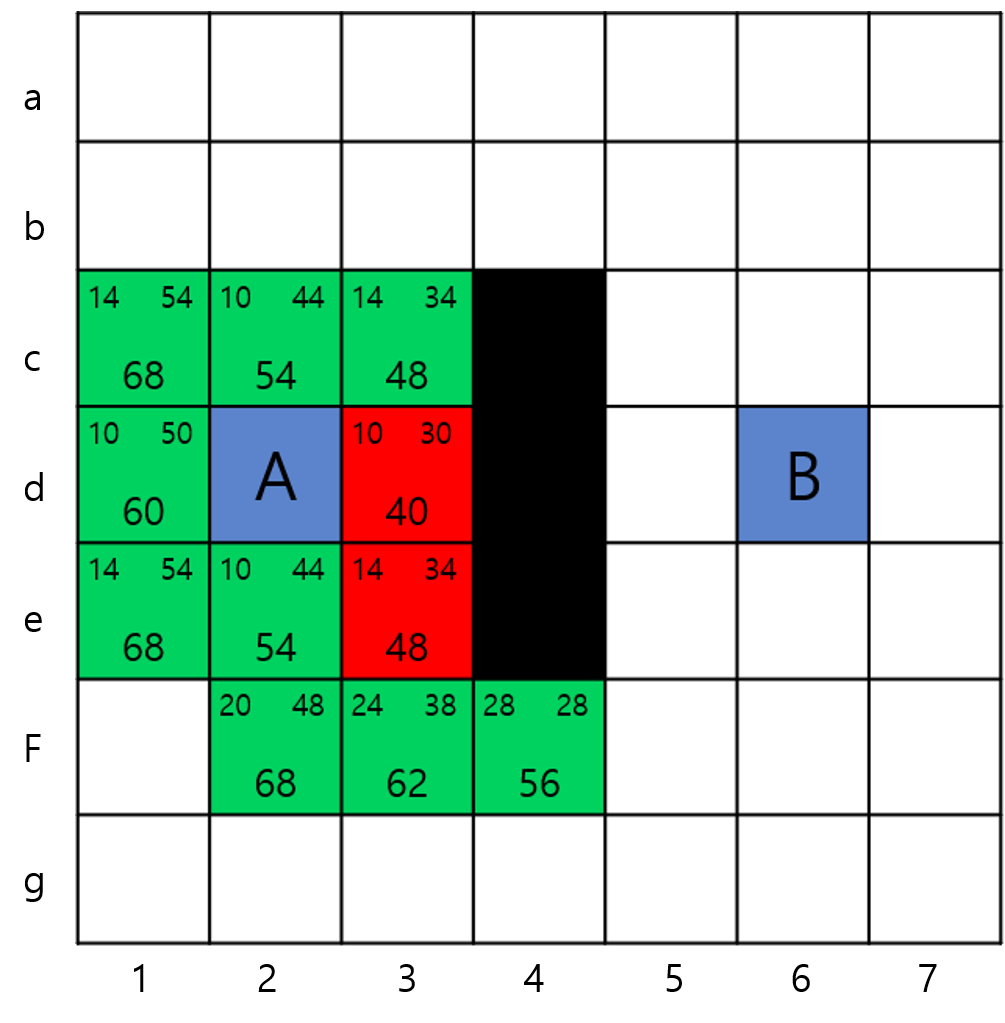
- 마찬가지로 OPEN에서 가장 작은 값을 가져온다. fCost값이 동일한 노드가 2개 이상일 경우 hCost의 값을 비교하여 작은 값을 가져온다. 이마저도 같다면 랜덤 또는 먼저 들어온 값을 계산하는 등의 방식으로 지정한다.
- neighbour = {f2, f3, f4}, 3개의 노드는 e3을 부모로 가진다. 이는 (f2, f3, f4) -> e3 -> d2 의 순서를 가진다는 뜻이다.
- OPEN = c1, c2, c3, d1, e1, e2, (-e3), (+f2, f3, f4)
- CLOSE = d2, d3 (+e3)
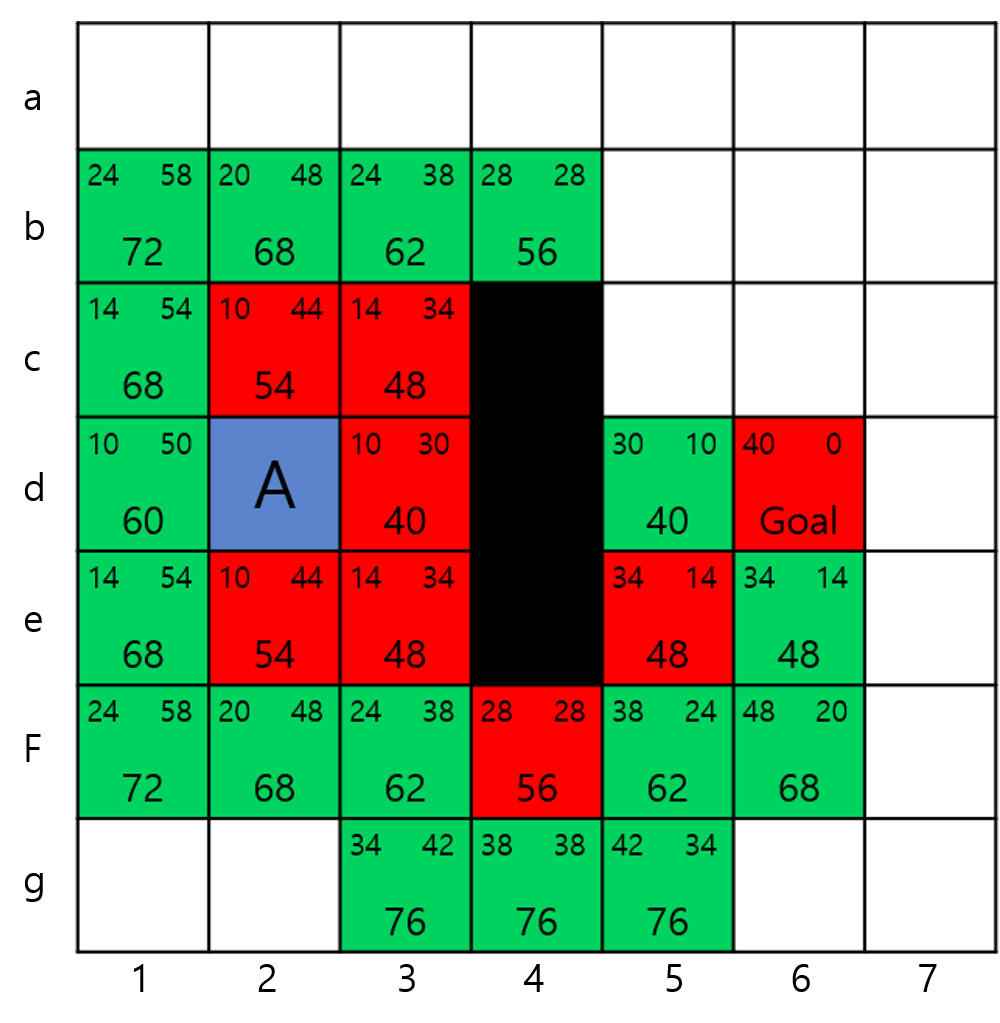
- 위 과정을 반복한 마지막 결과물이다.
구현(맵 생성)
게임 제작 엔진인 Unity 3D 에서 구현을 해보려고 한다. 범위를 지정하여 노드를 생성하고 마우스를 활용하여 조작하는 프로그램을 만들 것이다. (버젼 : 2019.4.f1)
Node 생성
정보를 저장할 스크립트를 생성해준다.
Node.cs
public class Node
{
public GameObject ground;
public bool walkable;
public int gridX;
public int gridY;
public Node(GameObject _ground, bool _walkable, int _gridX, int _gridY)
{
ground = _ground;
walkable = _walkable;
gridX = _gridX;
gridY = _gridY;
}
}
gridX와 gridY 2차원으로 구성된 공간의 위치를 저장할 변수이다. ground는 node를 저장하고 있는 게임오브젝트이다. walkable은 이동가능한지 판단하는 변수이다.
Grid 생성
Grid.cs
public GameObject groundPrefab; //바닥을 이룰 게임오브젝트(정사각형의 Quad를 사용)
GameObject parentGrid; //groundPrefab의 부모
public Vector2 gridWorldSize; //노드의 크기
Node[,] grid;
public void CreateGrid()
{
if (parentGrid != null)
Destroy(parentGrid);
parentGrid = new GameObject("parentGrid");
grid = new Node[(int)gridWorldSize.x, (int)gridWorldSize.y];
Vector3 worldBottomLeft = Vector3.zero - Vector3.right * gridWorldSize.x / 2 - Vector3.forward * gridWorldSize.y / 2;
for (int x = 0; x < (int)gridWorldSize.x; x++)
{
for (int y = 0; y < (int)gridWorldSize.y; y++)
{
Vector3 worldPoint = worldBottomLeft + Vector3.right * (x + 0.5f) + Vector3.forward * (y + 0.5f);
GameObject obj = Instantiate(groundPrefab, worldPoint, Quaternion.Euler(90, 0, 0));
obj.transform.parent = parentGrid.transform;
grid[x, y] = new Node(obj, true, x, y);
}
}
}
결과 화면
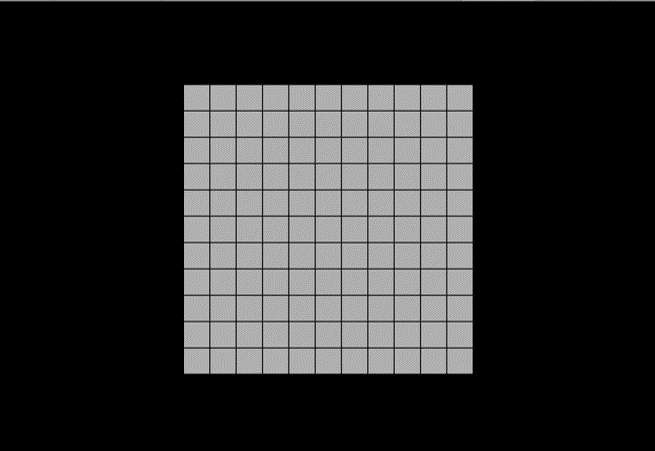
장애물 생성
마우스 클릭과 RayCast를 활용한 장애물 만들기
- 마우스 왼쪽 클릭을 입력 받는다.
- 카메라부터 Ray를 보내 ground 오브젝트를 확인한다.
- 해당 오브젝트의 node의 walkable 값을 반전시킨다.(true <-> false)
Setting.cs
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0)) //마우스 왼쪽 클릭을 할 때, true를 반환
{
Node node = RayCast();
//ChangeWalkable 코루틴을 실행
if (node != null) StartCoroutine("ChangeWalkable", node);
}
}
IEnumerator ChangeWalkable(Node node)
{
//처음 선택한 노드의 walkable 반대값을 가짐
bool walkable = !node.walkable;
while (Input.GetMouseButton(0)) //마우스 왼쪽 클릭을 누르고 있으면 true를 반환
{
node = RayCast();
if (node != null) node.ChangeNode = walkable;
yield return null;
}
}
public Node RayCast()
{
Ray ray = Camera.main.ScreenPointToRay(Input.mousePosition); //카메라를 기준으로 마우스커서의 위치로 발사한다.
RaycastHit hit;
if (Physics.Raycast(ray, out hit, 100f)) //rqy를 100f거리만큼 발사하여 맞은 Collider의 정보를 hit에 반환한다.
{
GameObject gronud = hit.collider.gameObject;
return grid.NodePoint(gronud.transform.position);
}
return null; //ray에 맞은 Collider이 없으면 null값을 반환
}
Grid.cs
//오브젝트가 위치하는 곳의 node를 찾아 반환하기 위한 함수
public Node NodePoint(Vector3 rayPosition)
{
int x = (int)(rayPosition.x + gridWorldSize.x / 2);
int y = (int)(rayPosition.z + gridWorldSize.y / 2);
return grid[x, y];
}
Node.cs
public bool ChangeNode
{
set
{
Color color = value ? Color.white : Color.gray;
walkable = value;
ground.GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().material.color = color; //선택된 오브젝트의 색을 바꾸는 부분
}
}
결과 화면
시작과 도착 지점 생성
시작과 도착 지점 노드 만들고 마우스로 위치를 조정할 수 있게 하기(마우스 드래그 활용)
- 마우스 클릭을 입력 받았을 때, 해당 노드가 Start, End 또는 둘다 아닌지 확인하기
- 해당 노드가 Start 또는 End 일 때, 마우스 드래그로 위치 이동하기
Node.cs
//새로운 변수 생성
public bool start;
public bool end;
public bool ChangeNode
{
set
{
Color color = value ? Color.white : Color.gray;
walkable = value;
ChangeColor = color;
}
}
public bool ChangeStart
{
set
{
if (value)
{
start = value;
ChangeColor = Color.Lerp(Color.blue, Color.white, 0.2f);
}
else
{
start = value;
ChangeNode = walkable;
}
}
}
public bool ChangeEnd
{
set
{
if (value)
{
end = value;
ChangeColor = Color.Lerp(Color.red, Color.white, 0.2f);
}
else
{
end = value;
ChangeNode = walkable;
}
}
}
public Color ChangeColor
{
set
{
ground.GetComponent<MeshRenderer>().material.color = value;
}
}
Setting.cs
void Update()
{
if (Input.GetMouseButtonDown(0) )
{
Node node = RayCast();
if (node != null)
{
if(node.start || node.end)
//반환받은 node가 Start, End 인지 확인
StartCoroutine("SwitchStartEnd", node);
else
StartCoroutine("ChangeWalkable", node);
}
}
}
IEnumerator SwitchStartEnd(Node node)
{
bool start = node.start;
Node nodeOld = node;
while (Input.GetMouseButton(0))
{
node = RayCast();
if (node != null && node != nodeOld)
{
if (start && !node.end)
{
node.ChangeStart = true;
nodeOld.ChangeStart = false;
nodeOld = node;
}
else if (!start && !node.start)
{
node.ChangeEnd = true;
nodeOld.ChangeEnd = false;
nodeOld = node;
}
}
yield return null;
}
}
결과 화면

구현(알고리즘 적용)
void FindPath()
{
List<Node> openSet = new List<Node>(); //OPEN
HashSet<Node> closedSet = new HashSet<Node>(); //CLOSE
openSet.Add(start); //OPEN에 시작노드 저장
while (openSet.Count > 0)
{
Node currentNode = openSet[0];
//OPEN에 fCOST가 가장 작은 노드를 찾기
for(int i = 1; i<openSet.Count; i++)
{
if (openSet[i].fCost < currentNode.fCost || openSet[i].fCost == currentNode.fCost && openSet[i].hCost < currentNode.hCost)
{
currentNode = openSet[i];
}
}
openSet.Remove(currentNode);
closedSet.Add(currentNode);
//도착지점에 오면 종료
if (currentNode == end)
{
return;
}
if (currentNode != start)
currentNode.ChangeColor = Color.Lerp(Color.cyan, Color.white, 0.2f);
//이웃 노드를 검색
foreach (Node neighbour in grid.GetNeighbours(currentNode))
{
//이동불가 노드 이거나 이미 검색한 노드 제외
if (!neighbour.walkable || closedSet.Contains(neighbour))
{
continue;
}
int newMovementCostToNeighbour = currentNode.gCost + GetDistance(currentNode, neighbour);
if (newMovementCostToNeighbour < neighbour.gCost || !openSet.Contains(neighbour))
{
neighbour.gCost = newMovementCostToNeighbour;
neighbour.hCost = GetDistance(neighbour, end);
neighbour.parent = currentNode;
if (!openSet.Contains(neighbour))
{
openSet.Add(neighbour);
if (neighbour.walkable && !neighbour.end)
neighbour.ChangeColor = Color.Lerp(Color.green, Color.white, 0.2f);
}
}
}
}
}
//노드간의 거리 계산
int GetDistance(Node nodeA, Node nodeB)
{
int dstX = Mathf.Abs(nodeA.gridX - nodeB.gridX);
int dstY = Mathf.Abs(nodeA.gridY - nodeB.gridY);
if (dstX > dstY)
return 14 * dstY + 10 * (dstX - dstY);
return 14 * dstX + 10 * (dstY - dstX);
}
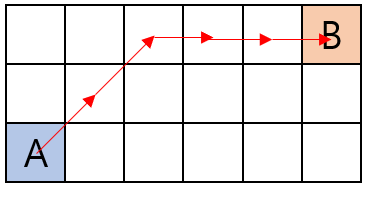
거리 계산하는 법
A와 B사이의 거리는 14 _ 2 + 10 _ 3 = 58이다.
public List<Node> GetNeighbours(Node node)
{
List<Node> neighbours = new List<Node>();
int[,] temp = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, 0 } };
bool[] walkableUDLR = new bool[4];
//상하좌우의 노드 먼저 계산
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int checkX = node.gridX + temp[i, 0];
int checkY = node.gridY + temp[i, 1];
if (checkX >= 0 && checkX < (int)gridWorldSize.x && checkY >= 0 && checkY < (int)gridWorldSize.y)
{
if (grid[checkX, checkY].walkable)
walkableUDLR[i] = true;
neighbours.Add(grid[checkX, checkY]);
}
}
//대각선의 노드를 계산
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
if (walkableUDLR[i] || walkableUDLR[(i + 1) % 4])
{
int checkX = node.gridX + temp[i, 0] + temp[(i + 1) % 4, 0];
int checkY = node.gridY + temp[i, 1] + temp[(i + 1) % 4, 1];
if (checkX >= 0 && checkX < (int)gridWorldSize.x && checkY >= 0 && checkY < (int)gridWorldSize.y)
{
neighbours.Add(grid[checkX, checkY]);
}
}
}
return neighbours;
}
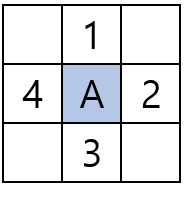
상하좌우의 노드를 위 순서대로 계산한다.
(1번 노드는 A위치를 기준으로 y + 1을 해준다. 2번 x + 1, 3번 y - 1, 4번 x - 1)
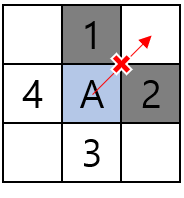
1번과 2번의 노드가 이동불가능하다면 3시방향의 대각선 노드 또한 이동이 불가능해야한다.
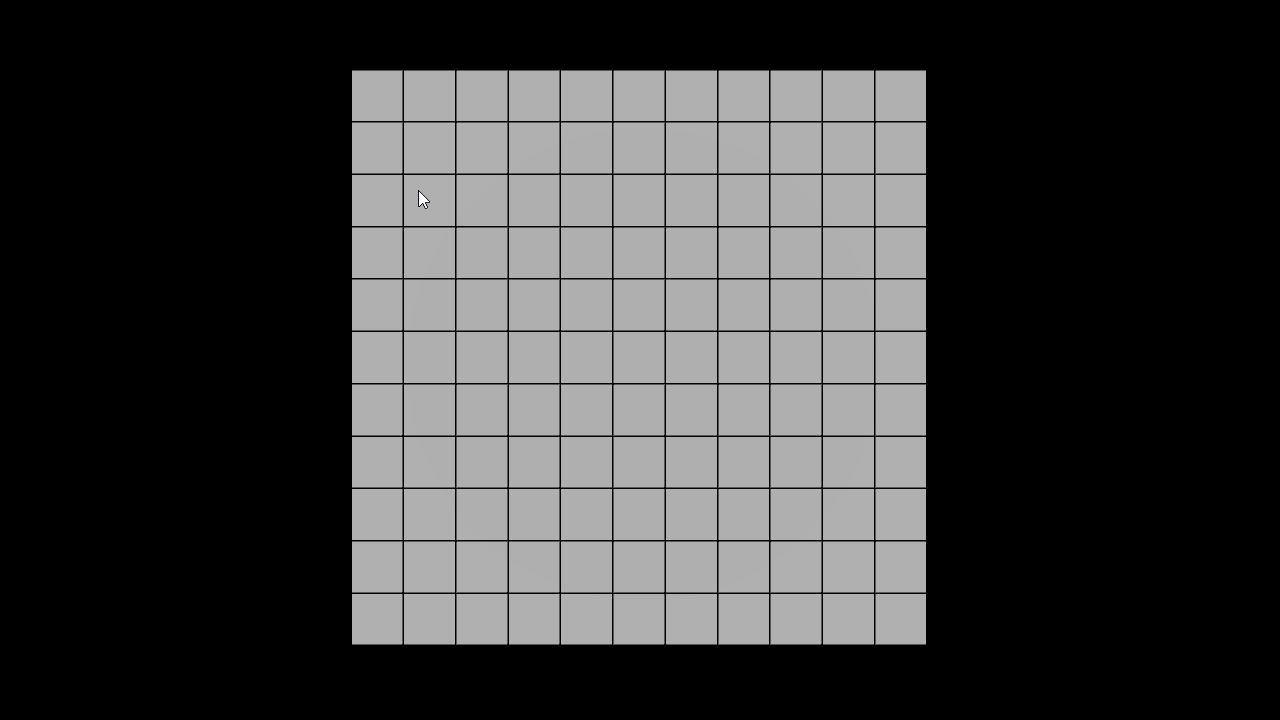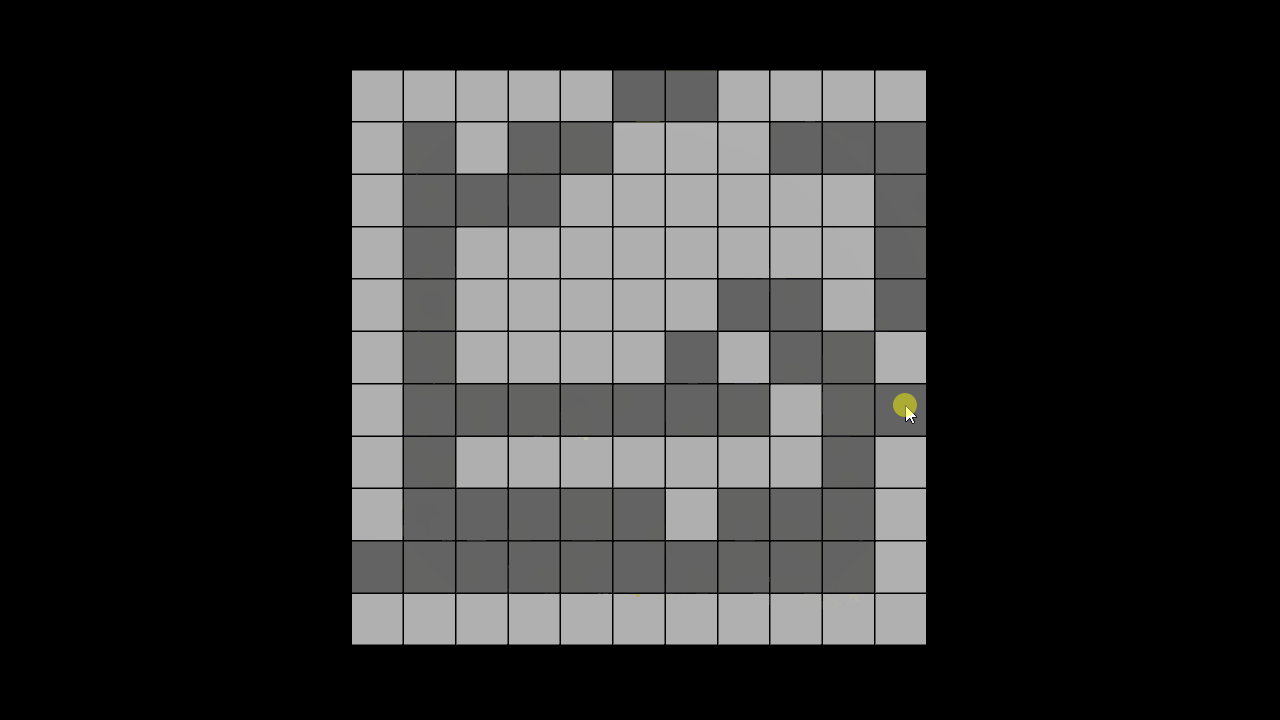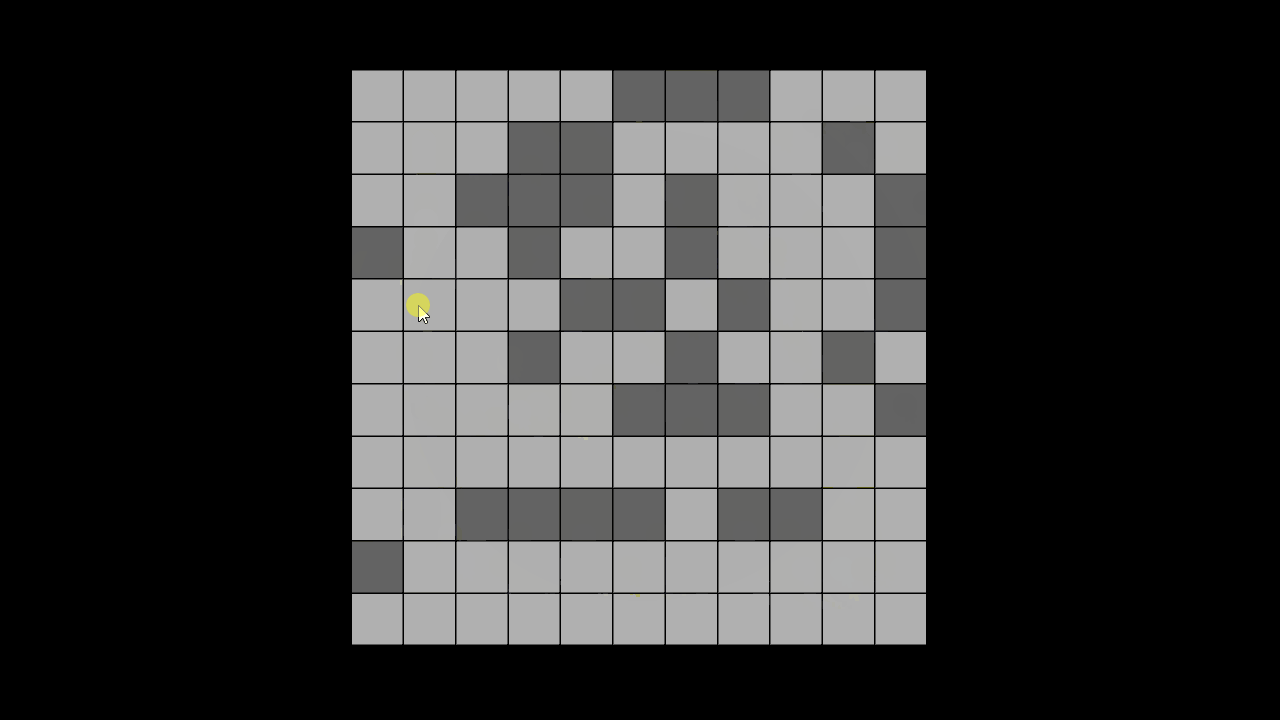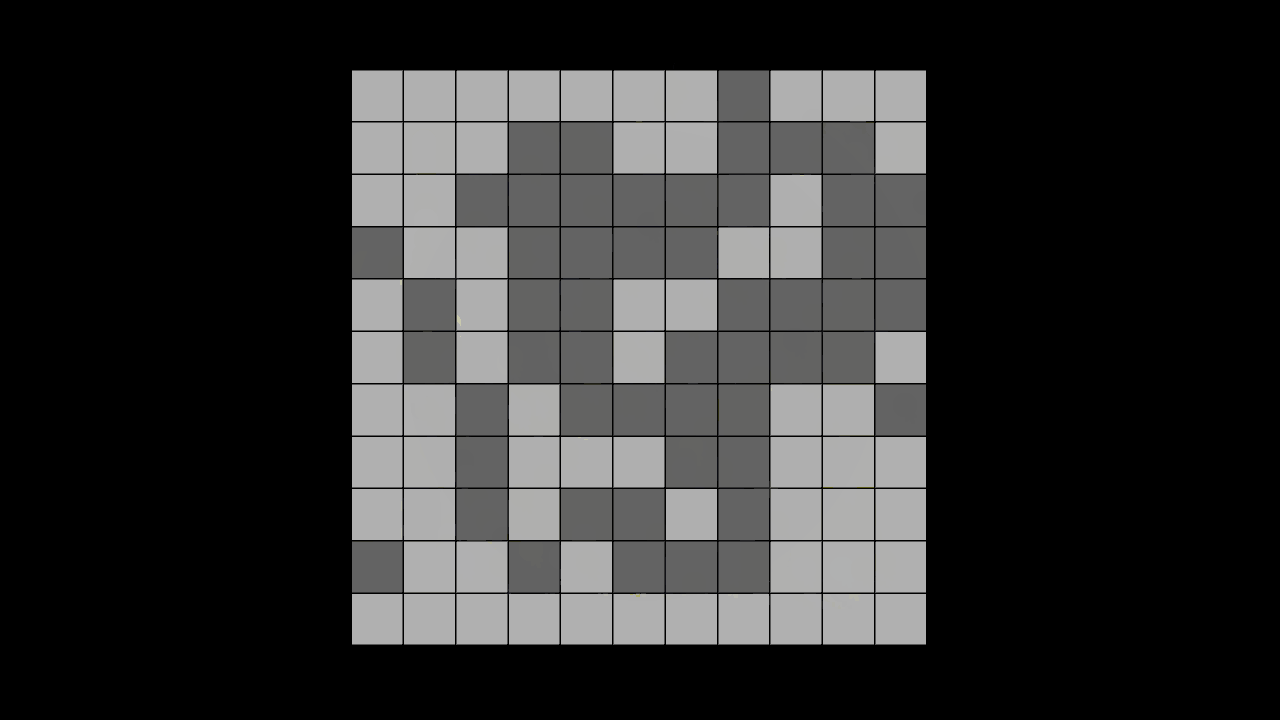
결과 화면

연두색 = OPEN, 하늘색 = CLOSE
웨이포인트 만들기
//도착지점 부터 출발지점까지 부모 노드를 입력하여 웨이포인트를 생성한다.
Vector3[] RetracePath(Node startNode, Node endNode)
{
List<Node> path = new List<Node>();
Node currentNode = endNode;
while (currentNode != startNode)
{
path.Add(currentNode);
currentNode = currentNode.parent;
}
Vector3[] waypoints = SimplifyPath(path);
Array.Reverse(waypoints);
return waypoints;
}
//반복되는 이동을 삭제해주며 웨이포인트를 간단하게 만든다.
Vector3[] SimplifyPath(List<Node> path)
{
List<Vector3> waypoints = new List<Vector3>();
Vector2 directionOld = Vector2.zero;
for (int i = 1; i < path.Count; i++)
{
Vector2 directionNew = new Vector2(path[i - 1].gridX - path[i].gridX, path[i - 1].gridY - path[i].gridY);
if (directionNew != directionOld)
{
waypoints.Add(path[i - 1].ground.transform.position + Vector3.up * 0.1f);
}
directionOld = directionNew;
}
waypoints.Add(start.ground.transform.position + Vector3.up * 0.1f);
return waypoints.ToArray();
}
결과 화면

GUI만들기
- 맵의 크기 조절이 가능하게 하는 부분 (TextField 2개와 버튼 1개)
- 검색 시작 - 재 시작 버튼
- 검색 멈춤 - 검색 취소 버튼
결과 화면